Songlines are traditional maps created by the Aboriginal tribes of Australia. These maps often appear more like beautiful elaborate paintings, but upon investigation, one discovers that the bright colors, circles, lines, and other various patterns are uniquely representative of a particular person, tribe, or place. Aboriginals believed that everything in nature existed in terms of the human existence developing around it, and that every human and tribe has their own song with similar elements that creates the world as they know it. These maps, though not particularly useful to the common man in this day in age, will forever be a beautiful cultural relic and a representation of truly original art, thinking, and map making of the Aboriginal culture.
Monday, April 25, 2011
Parallel Coordinate Graph
Parallel Coordinate Graph
Each variable in a parallel coordinate graph is applied to a vertical axis and data elements are plotted as connected sets of points, with one on each axis. In this 3D parallel coordinate view below, spatial and gene expression information are clearly separated while the basic character of spatial gene expression patterns is displayed in one dimension.
DLG Map
DLG
DLG maps are vector representations of planimetric and topographic map features. These features may be derived from cartographic source materials or from aerial photographs. DLG maps use manual and automated digitizing methods and on doing so, contain a wide variety of information from vegetation cover, to administrative boundaries, to roads, basic topography, and more. The DLG file below shows the transportation available for sale and the transportation in progress in the state of Illinois.
DLG maps are vector representations of planimetric and topographic map features. These features may be derived from cartographic source materials or from aerial photographs. DLG maps use manual and automated digitizing methods and on doing so, contain a wide variety of information from vegetation cover, to administrative boundaries, to roads, basic topography, and more. The DLG file below shows the transportation available for sale and the transportation in progress in the state of Illinois.
http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2003/of03-471/domier/index.html
DEM Map
DEM
 DEM maps, or Digital Elevation Models, are raster format maps that are produced by recording cartographic data, storing it, and processing the information into a cell of pixel. In this manner, digital files containing information about terrain elevations for ground positions at regularly spaced intervals are produced in a three dimensional format. The example map below shows a DEM of NYC, NY on November 12, 2003.
DEM maps, or Digital Elevation Models, are raster format maps that are produced by recording cartographic data, storing it, and processing the information into a cell of pixel. In this manner, digital files containing information about terrain elevations for ground positions at regularly spaced intervals are produced in a three dimensional format. The example map below shows a DEM of NYC, NY on November 12, 2003.Bilateral Graph Map
Bilateral Graph
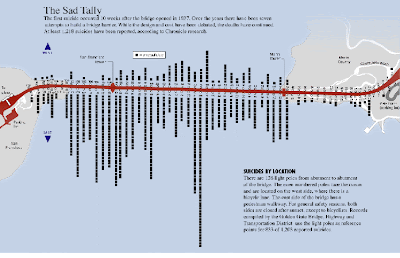 A bilateral graph is effective in displaying two related variables and how they differ in function. Bilateral graphs are visualization maps that show both increase and decrease on either side of the same map. The map below shows the statistics and results of Golden Gate Bridge jumpers. this graph shows the number of people that committed suicide by their location on the bridge, the east and west sides of the bridge coordinate to positive and negative sides of the graph. By viewing the graph, it can be observed that more jumps occur on the east side of the bridge
A bilateral graph is effective in displaying two related variables and how they differ in function. Bilateral graphs are visualization maps that show both increase and decrease on either side of the same map. The map below shows the statistics and results of Golden Gate Bridge jumpers. this graph shows the number of people that committed suicide by their location on the bridge, the east and west sides of the bridge coordinate to positive and negative sides of the graph. By viewing the graph, it can be observed that more jumps occur on the east side of the bridge Lorenz Curve Map
Lorenz Curve Map
Lorenz curve maps are useful in representing the degree of inequality that exists between distributions involving two variables. Often times, these curves represent the outcomes of incomes and wealth when they are distributed unequally throughout societies. The dashed lines in lorenz curves display how data would be if properties were evenly distributed and the solid dark line shows the actual distribution. As show in the example below, the area between the curve and the straight line represents the area of inequality.
Range Graded Proportional Circle Map
Range Graded Proportional Circle Map
Useful in representing discrete phenomena with abrupt variations. The data used in this format is usually representative of magnitudes. In the example map below, various sizes of circles and their nominal equivalents are overlaid on a map to represent varying magnitudes of American Indian Populations in different states in 1990. The placement of the circles over the map not only show where these populations reside, but they also easily visually convey the magnitude of each individual population community in doing so.
Correlation Matrix
A correlation map shows a symmetrical, semi-definite correlation matrix. Mostly, correlation matrices represent the correlation of change and time and are positive trending. In the example below, there is a symmetrical correlation matrix on analyzed enzymes and metabolites. The variations in shading accompanied by the given values, provide a clear visualization of the coefficients between the two traits.
Star Plot Map
Star Plot Map
Star Plot maps are valuable tools that help to visualize comparisons of multiple variables for each observation. In the star plot example below of 1979 automobiles, the data of 16 cars is plotted. Each line plotted represents a different feature found in every car and the length of the line represents the quality of that particular set of data. These features are aspects such as price, mileage, and weight to name a few. These star plots can be observed individually, or they may be observed as a group so that common characteristics can be compared. The separate spokes representing quantities are equal-angular and are called radii. The plot gets its star-like appearance when lines are drawn connecting values.
Star Plot maps are valuable tools that help to visualize comparisons of multiple variables for each observation. In the star plot example below of 1979 automobiles, the data of 16 cars is plotted. Each line plotted represents a different feature found in every car and the length of the line represents the quality of that particular set of data. These features are aspects such as price, mileage, and weight to name a few. These star plots can be observed individually, or they may be observed as a group so that common characteristics can be compared. The separate spokes representing quantities are equal-angular and are called radii. The plot gets its star-like appearance when lines are drawn connecting values.
Wind Rose Map
Wind Rose Map
Wind Rose Maps, visually display the distribution of wind direction. In this particular example from the NOAA website, the direction was recorded at one site for 24 hours. The percentage of time which the wind comes from a certain direction by the rings and the color changing represents the percentage of time which the wind came from that particular direction.
Wind Rose Maps, visually display the distribution of wind direction. In this particular example from the NOAA website, the direction was recorded at one site for 24 hours. The percentage of time which the wind comes from a certain direction by the rings and the color changing represents the percentage of time which the wind came from that particular direction.
Similarity Matrix Map
Similarity Matrix Maps such as the example below, are useful in providing quick visual assessments of how similar documents, terms, places, or data are. They are based on the level of similarity between results of data and use both numerical charts and the visual density of pixels in a chart form to characterize and display information.
Triangular Plot Map
Triangular Plot Map
Triangular Plot Mapping is useful in that it is able to display three dimensions or qualities of a given subject while also showing their relation to each other. In the example below, triangular mapping is used to show implications of correlations between skin color and genetic ancestry of West Africans, Europeans, and Indigenous people for biomedical research. From the triangle plot, it can be readily observed that the majority of humans come from some stem of West African descent.
Stem and Leaf Plot Map
Stem and Leaf Plot Map
Sunday, April 24, 2011
Histogram Map
Histogram Map
Histogram maps are useful in plotting the degree of density in a measurement of data over a given area. Histograms are unique in that they display tabulated frequencies, and in mapping, this makes the information easy to read as far as the density of results is displayed. In the example below, not only are the various heights of black cherry trees displayed, but it is easy to see the average height of the trees.
Histogram maps are useful in plotting the degree of density in a measurement of data over a given area. Histograms are unique in that they display tabulated frequencies, and in mapping, this makes the information easy to read as far as the density of results is displayed. In the example below, not only are the various heights of black cherry trees displayed, but it is easy to see the average height of the trees.
Box Plot Map
Box Plot Map
Box plots, also known as box and whisker diagrams, are a great way to simply display groups of numerical diagrams. They appear simpler than histograms or other charts displaying numerical information, but in their simplicity, they are preferred and useful because they make it very easy to determine outliers and differences in populations without making assumptions of the underlying statistical distribution. The example of a box plot below helps simplify and display the complicated results of an experiment in which the experimenter attempts to find a medium in which the true speed of light can be measured. The accuracy of the results over multiple attempts are displayed below along with their outliers.
3-D Scatter Plot Map
3-D Scatter Plot Map
3-D Scatter plot maps, employ the same method of one dimensional scatter plot maps in that they visualize numerical data and coordinate it with a trend in order to add ease to of interpretation to the viewer. However, multi-dimensional scatter plots differ in that they offer multiple degrees/ aspects of the same set of information and coordinate the trends all in one chart. The scatter plot below, for example, shows the percent of white per capita income on the depth of the Z axis, the percent of white degrees on the vertical Y axis, and the percent of white total population on the horizontal X axis. By adding the third dimension of the Z axis, and representing its depth in the variation in dot size, cartographers are able to add another element of measurement to the scatter plot.
Scatter Plot Map
Scatter Plot Map
Scatter plots are useful graphs for examining trends in large sets of data. They are excellent in displaying positive and negative correlations, trends, and outliers. The scatter plot below represents a trend in the percent of white degrees in comparison to the percent of the total white population.
Scatter plots are useful graphs for examining trends in large sets of data. They are excellent in displaying positive and negative correlations, trends, and outliers. The scatter plot below represents a trend in the percent of white degrees in comparison to the percent of the total white population.
Climograph Map
Climograph Map
A climograph map, such as the one below, is very useful in visualizing weather patterns in an areas over time. The Line and bar climograph map/chart below is able to use various techniques in one map to display temperature and precipitation over in Honolulu over the course of a year.
A climograph map, such as the one below, is very useful in visualizing weather patterns in an areas over time. The Line and bar climograph map/chart below is able to use various techniques in one map to display temperature and precipitation over in Honolulu over the course of a year.
Population Profile Map
Population Profile Map
Population Profile Maps, such as the map below of Texas' profile from the 2000 census, are quite useful tools in visualizing an area's population. The map below offers the population density for the state of Texas as well as many other factors pertinent to the population. These additional profile factors include a pie chart of the state's race breakdown, as well as charts indicating population by sex and age and housing tenure.
Univariate Choropleth Map
Univariate Choropleth Map
A univariate Choropleth map, simply stated, is a choropleth map that only represents one specific value over a given area. Univariate choropleth maps are valuable in their simplicity. By representing only one factor, such as the example map below of burnside, the obeserver can clearly indicate changes in the data over space.
A univariate Choropleth map, simply stated, is a choropleth map that only represents one specific value over a given area. Univariate choropleth maps are valuable in their simplicity. By representing only one factor, such as the example map below of burnside, the obeserver can clearly indicate changes in the data over space.
Bivariative Choropleth Map
Bivariative Map
The BI in Bivariative choropleth maps means that they, unlike regular choropleth maps, display two variable on the same image. These bivariative choropleth maps may consist of point features, line features or polygon features. The bivariative map below shows not only the median house value over a region as indicated by the dot density, but also employs color change to indicate the population over the same area.
Classed Choropleth Map
Classed Choropleth Maps
Classed Choropleth Maps, in contrast to unclassified choropleth maps, display information in colors but also provide more information about variations, this can be done in a number of ways. Below are a few examples, most classification is either categorical or numerical (nominal or interval). Depending on the information being displayed, the map maker may choose to classify in a number of categories, but most classified choropleth maps have 4- 6 different classes.
Unclassed Choropleth Map
Unclassed Choropleth Map
Choropleth maps are one of the most popular forms of displaying geographic information. The unclassed choropleth map, as opposed to the classed choropleth map, has the advantage of fluidly displaying information. The map below displays changes in elevation using color but does not provide any numerical data or strict lines of nominal change.
DOQQ Map
DOQQ Map
Digital Orthophoto Quarter Quads (DOQQs) maps are produced by the USGS. These digital aerial images contain orthorectified aerial photography as a resolution of 1 meter. These maps are useful in displaying satellite imagery of different types of vegetation. The map below is a DOQQ map of flowers in New England.
DRG Map
DRG Map
A DRG Map, or Digital Raster Graphic Map, uses the U.S. Geological Survey standard series. It is a scanned image of this USGS topographic series which includes all map collar information. The image is georeferenced to the surface of the Earth according to the Mercator projection. Therefore, the image matches the accuracy and datum of the source map. These maps, such as the ones below are particularly useful because they are accurate to the common Mercator projection scale, and at the same time, employ precise satellite imaging techniques.
http://topomaps.usgs.gov/drg/
A DRG Map, or Digital Raster Graphic Map, uses the U.S. Geological Survey standard series. It is a scanned image of this USGS topographic series which includes all map collar information. The image is georeferenced to the surface of the Earth according to the Mercator projection. Therefore, the image matches the accuracy and datum of the source map. These maps, such as the ones below are particularly useful because they are accurate to the common Mercator projection scale, and at the same time, employ precise satellite imaging techniques.
http://topomaps.usgs.gov/drg/
Isopleths
Isopleth Maps
An isopleth map is the general term used to describe any map which employs lines or colors to indicate areas with similar regional aspects. In this sense, isopachs, isobars, and many others are all isopleth maps. Isopleth maps are helpful in visually simplifying one general patch of information of a broad area. In the map below, color variations as well as number values are used to depict the pH levels of hydrogen ion concentrations throughout the U.S. and it is easy to determine with only a glance that the pH is higher on the west side of the country.
An isopleth map is the general term used to describe any map which employs lines or colors to indicate areas with similar regional aspects. In this sense, isopachs, isobars, and many others are all isopleth maps. Isopleth maps are helpful in visually simplifying one general patch of information of a broad area. In the map below, color variations as well as number values are used to depict the pH levels of hydrogen ion concentrations throughout the U.S. and it is easy to determine with only a glance that the pH is higher on the west side of the country.
Isopach Map
Isopach Map
An Isopach map is a form of and Isoline map that uses lines to illustrate variations of thickness. The contour lines of isopachs represent lines of equal thickness of a quality of the land within a tabular unit or stratum. In the map below, isopachs are employed to display the varying layers of thickness in mineral coal throughout a region.
An Isopach map is a form of and Isoline map that uses lines to illustrate variations of thickness. The contour lines of isopachs represent lines of equal thickness of a quality of the land within a tabular unit or stratum. In the map below, isopachs are employed to display the varying layers of thickness in mineral coal throughout a region.
Isohyet Map
Isohyet Map
In isohyetal maps, the spatial representation is of the amount of precipitation over a given area and time. Isohyetal maps use color as opposed to lines. The shading of areas, with labeled color bars, is accompanied by labeled isohyet sections as in the example below, which displays the percentage of precipitation in 1998 throughout the state of California.
In isohyetal maps, the spatial representation is of the amount of precipitation over a given area and time. Isohyetal maps use color as opposed to lines. The shading of areas, with labeled color bars, is accompanied by labeled isohyet sections as in the example below, which displays the percentage of precipitation in 1998 throughout the state of California.
Isotach Maps
Isotach Map
An Isotach map, also commonly known as a wind map, is another type of isoline map that specifically displays areas that display equal wind speed patterns and pressure. In the map below, wind patterns along the U.S. coastline can be readily observed with a glance and the speed of the wind velocity is displayed in miles per hour as well.
Isobar Maps
Isobar Maps
Where Isoline maps represent areas of a number of different equivalences, isobar maps have lines representing areas of equal pressure. When constructing isobar maps, a few general rules are followed, these include the fact that the isobars may not touch or cross. Isobars may only pass through areas in intervals of + or - 4 millibars, and that the atmospheric pressure is always given in terms of millibars. Also, since pressure lines are normally corrected for sea level, differences in pressure due to altitude are ignored. The map below displays the isobars representing the average differences in atmospheric pressure across the United States for September of 1998.
http://www.uwlax.edu/faculty/skala/Air-Pressure.htm
Where Isoline maps represent areas of a number of different equivalences, isobar maps have lines representing areas of equal pressure. When constructing isobar maps, a few general rules are followed, these include the fact that the isobars may not touch or cross. Isobars may only pass through areas in intervals of + or - 4 millibars, and that the atmospheric pressure is always given in terms of millibars. Also, since pressure lines are normally corrected for sea level, differences in pressure due to altitude are ignored. The map below displays the isobars representing the average differences in atmospheric pressure across the United States for September of 1998.
http://www.uwlax.edu/faculty/skala/Air-Pressure.htm
LIDAR
LIDAR Maps
LIDAR, also known as LADAR maps employ remote sensing technology in order to measure properties such as distance of a target area of land by illumination. Light Detection and Ranging technology uses pulses from a LASER and is sometimes called "LASER radar" in military contexts. The example of a LIDAR map below shows the flooding of New Orleans as a result of hurricane Katrina. Using infrared satellite and LASER technology, scientists can observe to what extent and depths the flooding reached throughout the city, making this technology and style of mapping a vital tool in natural disaster search and rescue situations.
LIDAR, also known as LADAR maps employ remote sensing technology in order to measure properties such as distance of a target area of land by illumination. Light Detection and Ranging technology uses pulses from a LASER and is sometimes called "LASER radar" in military contexts. The example of a LIDAR map below shows the flooding of New Orleans as a result of hurricane Katrina. Using infrared satellite and LASER technology, scientists can observe to what extent and depths the flooding reached throughout the city, making this technology and style of mapping a vital tool in natural disaster search and rescue situations.
Doppler Radar
Doppler Radar Map
Doppler Radar maps are constructed, often by meteorologists, by making use of satellite imagery and the Doppler radar effect. This specialized radar uses microwave signals to produce velocity data about a desired object at a distance. The reflection is noted and analyzed from the feedback of the microwave and a signal is returned to a radar giving information about the object's motion. This variation is highly accurate and is used most commonly for meteorological purposes as in the mapped image below of weather patterns in the south eastern United States, but is also employed for uses in radiology, aviation, and police speed guns.
Doppler Radar maps are constructed, often by meteorologists, by making use of satellite imagery and the Doppler radar effect. This specialized radar uses microwave signals to produce velocity data about a desired object at a distance. The reflection is noted and analyzed from the feedback of the microwave and a signal is returned to a radar giving information about the object's motion. This variation is highly accurate and is used most commonly for meteorological purposes as in the mapped image below of weather patterns in the south eastern United States, but is also employed for uses in radiology, aviation, and police speed guns.
Black & White Aerial Photo
Black & White Aerial Photograph
Aerial Photographs are often taken from a helicopter above a land mass and sometimes from satellite images. Such photos are often used for resource planning, mapping, and agricultural monitoring among other things. Black and white aerial photographs, like the one pictured below of intersecting interstate highways, are often more preferred because of their ability to display strict contrasts and details, also, an NHAP black and white photograph covers more area, about 129 square miles than a color-infrared photograph, which usually on covers about 68 square miles in a given shot. This difference in scope is attributed to the longer focal length in the color-infrared camera.
Infrared Aerial Photo
Infrared Aerial Photo
Infrared Aerial photographs are taken from satellites and use infrared film and digital sensors that are sensitive to a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. With the use of exact filtration and processing, they provide valuable information such as specific vegetation, land, and water usage, among a multitude of other things. The infrared photograph to the right shows the different vegetation and water polution in the Sacramento Deep Water Channel in Sacramento, California.
http://www.aerialarchives.com/infrared.htm
Infrared Aerial photographs are taken from satellites and use infrared film and digital sensors that are sensitive to a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. With the use of exact filtration and processing, they provide valuable information such as specific vegetation, land, and water usage, among a multitude of other things. The infrared photograph to the right shows the different vegetation and water polution in the Sacramento Deep Water Channel in Sacramento, California.
http://www.aerialarchives.com/infrared.htm
Cartographic Animations
Cartographic Animations
Cartographic animation maps are wonderful tools to display changes in an area over time. Though they have the downfall that they can only be used digitally because of the animation, they are a great alternative to viewing multiple maps of an area, and offer the viewer a chance to see the progress of a situation. The map below is a time lapse animation map which shows changes in Earth's wind velocity over the course of a year.
Cartographic animation maps are wonderful tools to display changes in an area over time. Though they have the downfall that they can only be used digitally because of the animation, they are a great alternative to viewing multiple maps of an area, and offer the viewer a chance to see the progress of a situation. The map below is a time lapse animation map which shows changes in Earth's wind velocity over the course of a year.
Statistical Map
Statistical Map
Cartogram Map
Cartogram maps are not so concerned with geographic accuracy of features such as the size and area of the land being mapped as they are about clearly displaying data. The map below is a cartogram map whose purpose is to display the allotment of electoral votes. This data is based off of population, therefore, though it is known that the District of Columbia is obviously not the same size as say, Montana or South Dakota, it is represented as such on this map because the data is the most important feature being displayed in cartogram maps and in this case, the population data is what takes importance in the matter of election statistics.
Flow Map
Flow Map
Flow maps are useful in mapping the flow, or the trend, of a number of things, be it people, goods, ideas, diseases, etcetera. The flow map below, produced by TeleGeography, maps the volume of international telephone traffic between nations in the European union. The area of the circles on the map represent the county totals and the thickness of the connecting lines represent the route totals in millions of minutes. It can be easily seen by this mapping technique that the majority of international calls are going in and out of the UK, Denmak, and France.
Isoline Map
Isoline Map
Isoline maps use contour lines to join points of the same value. Often times, these lines represent areas of equal rainfall, altitude, wind direction, and barometric pressure among other things. In the map below, isolines are used to indicate average annual precipitation in the state of New York over the past 25 years, the numbers on the isolines represent the rainfall in inches per year.
Isoline maps use contour lines to join points of the same value. Often times, these lines represent areas of equal rainfall, altitude, wind direction, and barometric pressure among other things. In the map below, isolines are used to indicate average annual precipitation in the state of New York over the past 25 years, the numbers on the isolines represent the rainfall in inches per year.
Proportional Circle Map
Proportional circle maps use circles imposed over a geographical area to represent numerical and proportional data. By applying a formula to control the area of the circles, the size of the circle reflects the amount of data over that area. The map below is a proportional circle map showing the Filipino population in the south eastern U.S. in the year 2000. Without even reading the numerical values, it can be easily seen that the largest percentage of Filipinos in the United States live in West Virginia, Florida, and Texas.
Choropleth Map
Choropleth Map
The word choropleth derives from the Greek words for "area/region" and "multiply." A choropleth map is a thematic map which uses coloring or shading pattern techniques to display the measurement of some sort of statistical data over a region. Often times, it is political data being displayed because this is an easy way to readily see the changes in statistical data over an area. The map below is an example of a choropleth map showing the results of the 2004 U.S. presidential election.
Dot Distribution Map
Dot Distribution Map
Dot distribution maps use dots to show the density of information over a region. The map below is a dot distribution map of the U.S. population in 2000. The map was distributed by the U.S. census bureau and is commonly referred to as the "Nightime Map" because the white dots, representing the population of an area, are also similar to the amount of light that might be distributed by these areas at night because of the amount of people there.
Propaganda Map
Propaganda Map
All maps lie to some extent because of the nature of the Earth's surface and the fact that it can not be accurately represented on a flat paper. Propaganda maps however, differ in this respect in that they lie intentionally in order to deceive. Many propaganda maps, like the one shown here, are created during wartime in order to make the public have a skewed sense of reality of the current situation. The map below is a sort of propaganda map inspired by Wir Sind Spartacus timeline.
Hyposymetric Map
This Topographic hypsometric map is of Goiani's Metropolitan Region. Hypsometric maps use color variations to represent changes in terrain elevation. In this particular map, The highest mountain peaks are represented with white shading and contour lines around the mountains represent points of equal elevation.
Saturday, April 23, 2011
PLSS Map
PLSS Map
A PLSS map, also known as a Public Land Survey System map, is a map that is created by the U.S. government and used to divide and describe public land domains.This rectangular system of surveys can be used to divide all public land in the U.S. These segments are usually in portions of 6 square miles. The map below is a PLSS map of the principle meridians and baselines produced by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management.
Cadastral Map
Cadastral Maps
Cadastral maps show boundaries and ownership of land parcels. The map below is a cadastral map with boundaries outlined in red imposed over and aerial image of the coastal zone of Gagra Georgia. Cadastral maps are useful for individuals or companies looking to purchase or develop land. A map such as the one below, since it is an aerial image as well, would be very useful not only for individuals but for government, developers, and real estate agencies as well.
Cadastral maps show boundaries and ownership of land parcels. The map below is a cadastral map with boundaries outlined in red imposed over and aerial image of the coastal zone of Gagra Georgia. Cadastral maps are useful for individuals or companies looking to purchase or develop land. A map such as the one below, since it is an aerial image as well, would be very useful not only for individuals but for government, developers, and real estate agencies as well.
Thematic Map
Thematic Maps
Thematic maps, as the name indicates, use color and pattern techniques to display a theme throughout a place. The map below includes multiple themes throughout Florida such as precipitation, land use, and transportation to name a few. Various shades help to display reliefs in physical features and included in this map are the themes of change over time as well as various labels of major cities and other points of political and geographic importance.
Topographic Map
ToPogRaPhIc mApS
In contrast to the previously posted planimetric map of Tallahassee, this map below is a topographic map of the city. Where the last map would have been useful as an easy means of finding direct routes by street names, topographic maps display physical features in the Earth's surface such as hills, mountains, and elevation changes. These maps are quite useful when planning to bike or hike trails and can reveal a great deal of useful information about a landscape. Many topographic maps also offer information such as exact numbers of elevation change.
http://www.topozone.com/map.asp?lon=-84.2807329&lat=30.4382559&datum=nad83
Planimetric Map
Planimetric Map
Plain and simple, planimetric maps show no relief. These types of maps, such as the one below of a portion of Tallahassee, only offer one dimension. Planimetric maps can be useful in figuring out direct road routes, but since they show no topographic features, this could be a problem if one needs to get around hills on their bike for instance. They show accurate horizontal distances between features and locations, but they lack topographic information.
Mental Maps
MENTAL MAPS/MAPPING
Mental Maps, like all maps, are constructs of the human mind. It is ironic and interesting in itself that we can see images of mental mapping, but what makes mental maps separate from any other form of mapping is that they are presented in terms of an individual's imagination, and are never wrong or distorted in the respect that they are used in the mind of the beholder and in terms relative to and for that individual.
Mental mapping (though contradictory in that we have physical examples images of these abstract mental constructs here) are in the mind of the creator, and stored for the familiarity and convenience of the individual.
Mental maps like the one below, can be of abstract ideas, such as the organization of time management...
http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newISS_01.htm...or, they may simply be depictions of a physical location, but only constructed with relative importance to the individual in mind.
http://blog.mywonderfulworld.org/2010/05/create-a-mental-map-of-your-community.html
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

